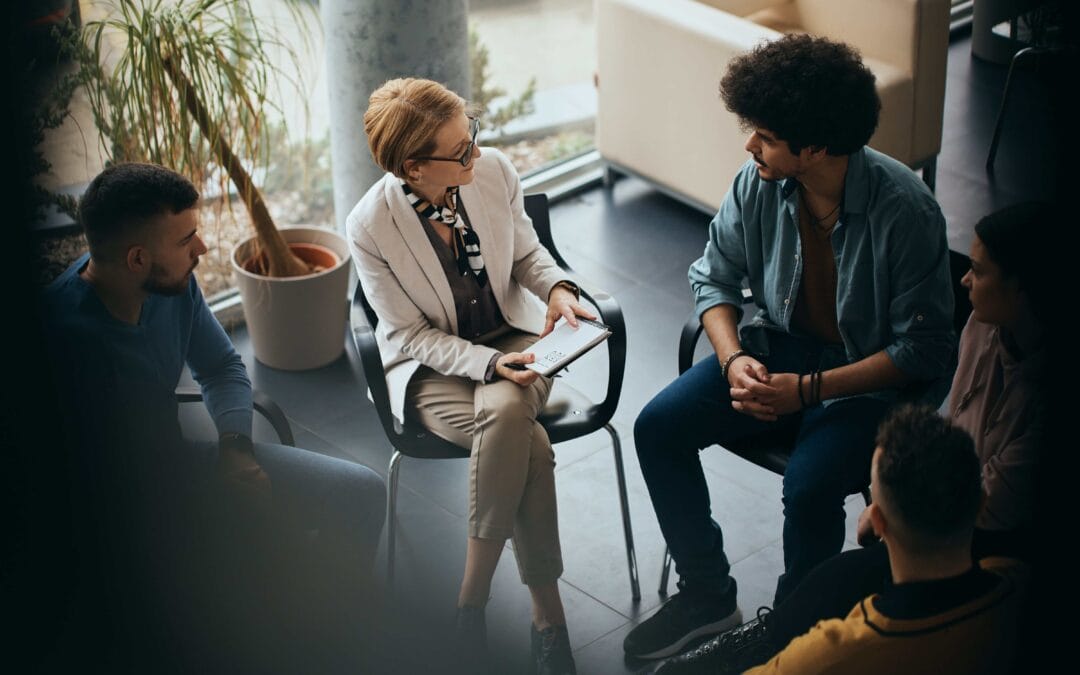
Why is Alcoholism Considered a Chronic Disease?
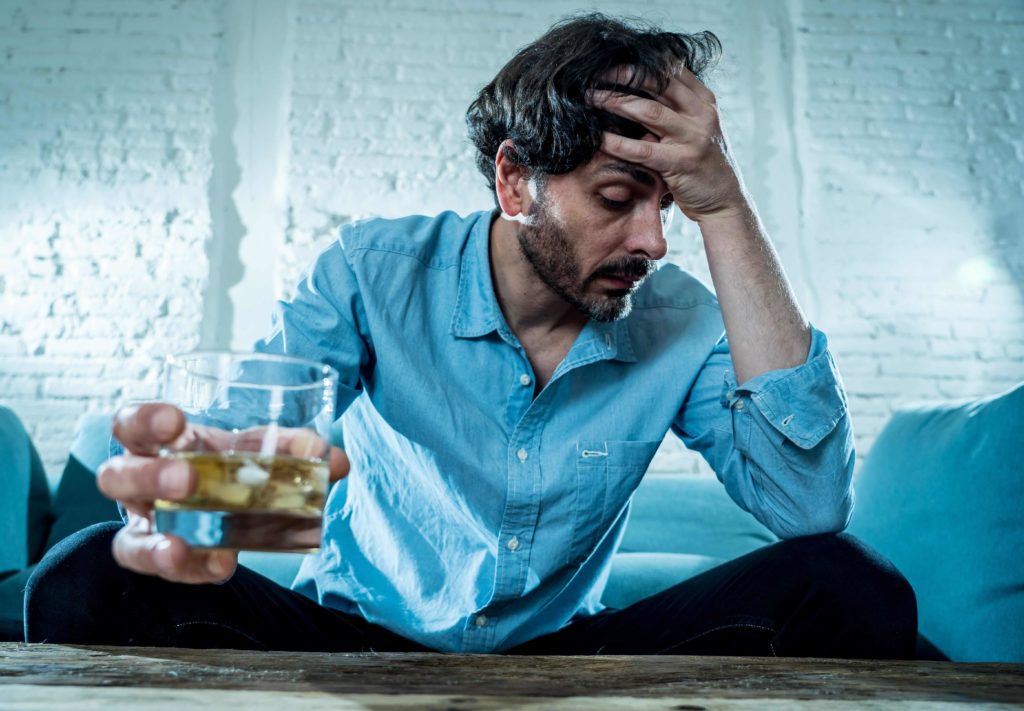 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) define chronic disease as a health condition that lasts a year or longer. With lifestyle changes, medications, and other therapies, chronic disease can typically be managed, but not cured. Without intervention, chronic diseases tend to worsen over time and are often fatal.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) define chronic disease as a health condition that lasts a year or longer. With lifestyle changes, medications, and other therapies, chronic disease can typically be managed, but not cured. Without intervention, chronic diseases tend to worsen over time and are often fatal.
Chronic diseases are the leading cause of death and disability in the U.S., accounting for about 70 percent of all deaths. The CDC cites the major risk factors for chronic disease as tobacco use, lack of physical exercise, poor nutrition, and excessive alcohol use.
Defining Alcohol Use Disorder
The American Medical Association (AMA) first identified alcoholism as a disease in 1956. In 1980, the American Psychiatric Association identified substance use disorder as a primary mental health disorder and included alcoholism as a subset of personality disorders.
In 1992, the AMA published the following definition of alcoholism,
“Alcoholism is a primary, chronic disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations. The disease is often progressive and fatal. It is characterized by continuous or periodic: impaired control over drinking, preoccupation with the drug alcohol, use of alcohol despite adverse consequences, and distortions in thinking, most notably denial.”
The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) updated its definition of addiction in 2018 to, “a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual’s life experiences.”
Today, alcoholism, alcohol abuse, and alcohol addiction are classified in the current Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) as alcohol use disorder (AUD) or substance use disorder (SUD). The DSM-5 is published by the American Psychiatric Association as a reference manual for professional diagnosis of mental disorders, including alcohol and substance use disorders. The manual offers specific criteria to determine if the disorder is at a mild, moderate, or severe stage.
Characteristics of Chronic Disease
According to the National Health Council, the most prevalent chronic conditions in the U.S. include cancer, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, heart disease, pulmonary conditions, and mental illness (which includes alcohol and substance use disorders).
Characteristics of AUD and other chronic diseases often include:
- Develops over a period of time
- Condition is not communicable
- Does not heal spontaneously
- Results in impaired function and progressive disability
- Worsens over time without intervention and may lead to other adverse health conditions, and death
- Can be managed with treatment, but there is no cure
Alcohol Use Disorder also involves some characteristics common to addiction, but not typically found with most other chronic diseases. Alcohol or drug addictions affect the pleasure, reward, and motivation systems of the brain. Prolonged use of the addictive substance alters brain chemistry, leading to physical, emotional, mental, and social dysfunction. If the addictive substance is discontinued, withdrawal symptoms typically occur.
Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder
As with all chronic diseases, treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder is a lifelong process. Learning to manage triggers and commit to a healthy lifestyle without alcohol has enabled many suffering from AUD to enjoy a long, fulfilling life in recovery.
Treatment offering the greatest potential for successful recovery includes behavioral therapies, medication, a 12-step support system, and family support. Studies show that those who continue therapy after completing their treatment program and regularly attend 12-step support meetings, have the highest success rate for long-term recovery.
Reviewed and Assessed by
Taylor Brown, B.A.Com., MAADC II
Tim Coleman, M. of Ed.